Random Walk in Python
1. Introduction
This is an article about random walk in python. It’s a process that explains the path which is made of random steps in sequence. A simple example is on the integers number line. Integers start from 0 and each step is either -1 or +1 with a probability of 50%. The complex examples are molecules moving in a gas, stock price fluctuations, and the search path of prey by a carnivorous animal.
2. Random Walk
2.1 Prerequisites
Python 3.6.8 is required on windows or any operating system. Pycharm is needed for python programming.
2.2 Download
Python 3.6.8 can be downloaded from the website. Pycharm is available at this link.
2.3 Required Libraries
2.3.1 Python Setup
To install python, the download package or executable needs to be executed.
2.4 IDE
2.4.1 Pycharm Setup
Pycharm package or installable needs to be executed to install Pycharm.
2.5 Launching IDE
2.5.1 Pycharm
Launch the Pycharm and start creating a pure python project named HelloWorld. The screen shows the project creation.
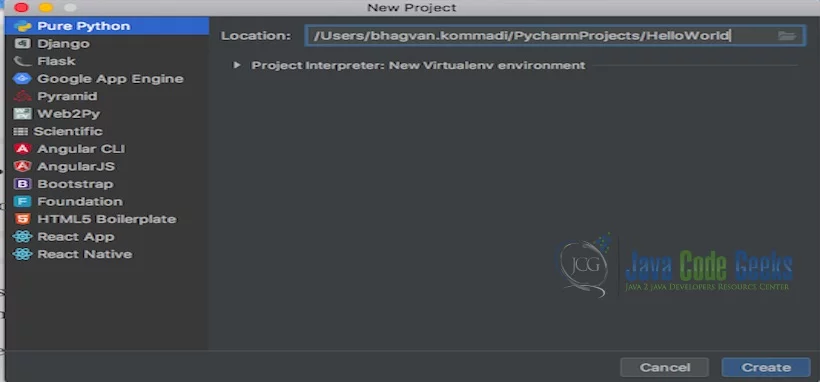
The project settings are set on the next screen as shown below.
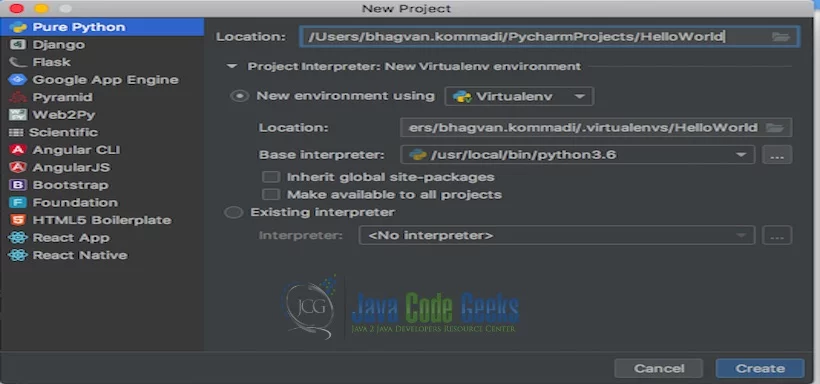
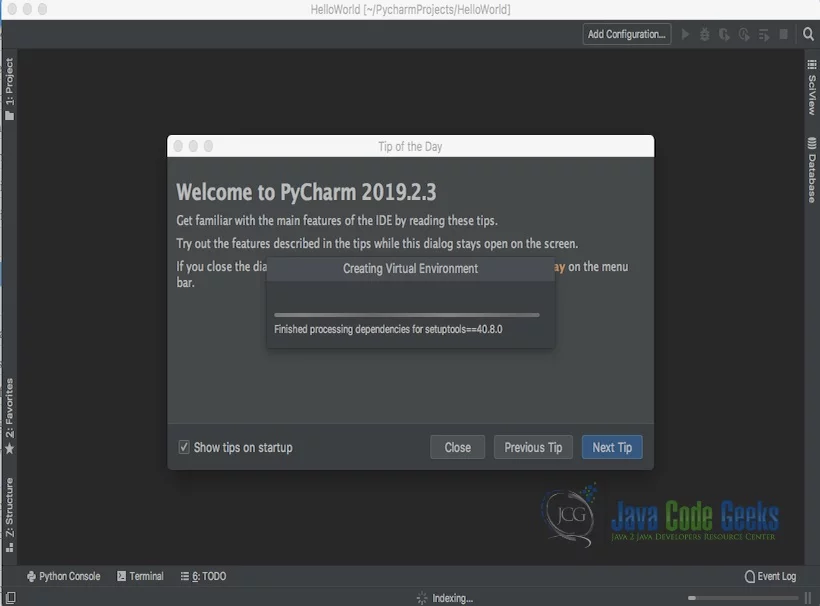
Pycharm welcome screen comes up and shows the progress as indicated below.
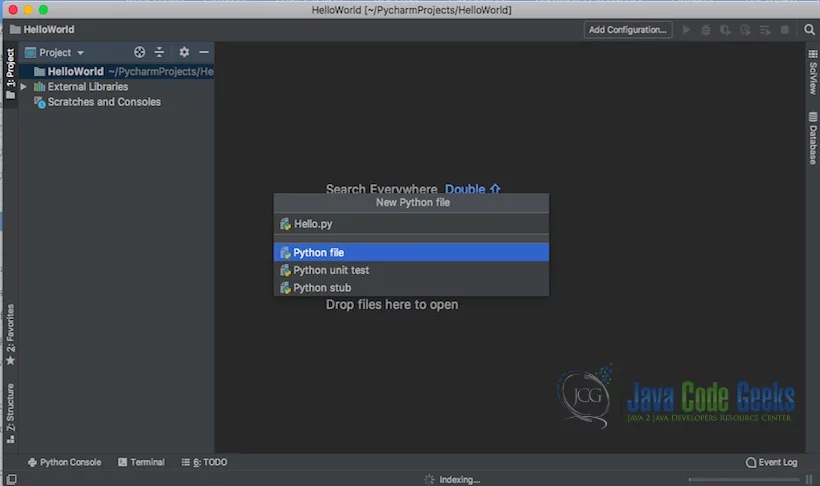
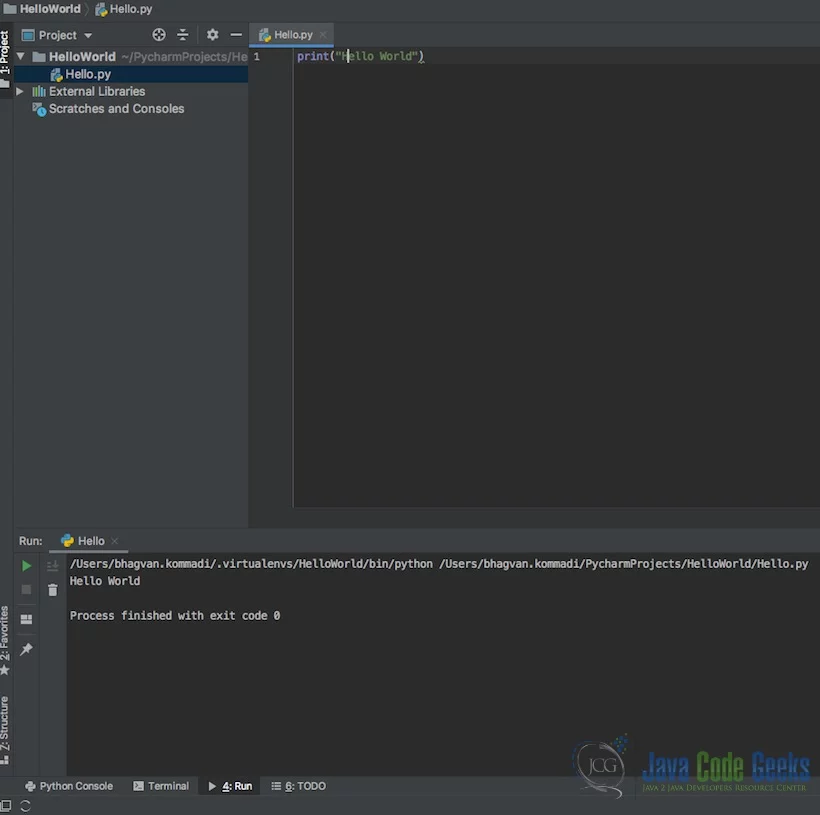
You can create a Hello.py and execute the python file by selecting the Run menu.
The output message “Hello World” is printed when the python file is Run.
2.6 One Dimensional Random Walk
Let us start with a one-dimensional walk. The steps are taken in only two directions. It can be right or left on the x-axis. It can also be up or down on the y-axis. The code below shows how to implement the one-dimensional random walk.
One Dimensional Random Walk
import numpy as nump
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
def SingleDimensionRandomWalk(n):
x = 0
y = 0
xposition = [0]
yposition = [0]
for i in range (1,n+1):
step = nump.random.uniform(0,1)
if step 0.5:
x += 1
y += -1
xposition.append(x)
yposition.append(y)
return [xposition,yposition]
OneDRandomWalk = SingleDimensionRandomWalk(2345)
plot.plot(OneDRandomWalk[0],OneDRandomWalk[1],'r-', label = "RandomWalk1D")
plot.title("One Dimensional Random Walks")
plot.show()
You can execute the above code with the command below:
Execution Command
python3 single_dimension_random_walk.py
The output is the plot which is shown below:

2.7 Two-Dimensional Random walk
Now let us see the implementation of a two-dimensional walk. Two-dimensional can be North, South, West, and East directions on the x and y-axis. The implementation is shown below in the code snippet.
Two Dimensional Random Walk
import numpy as nump
import pylab as pythonlab
import random as pyran
n = 2345
x = nump.zeros(n)
y = nump.zeros(n)
steps=["NORTH","SOUTH","EAST","WEST"]
for i in range(1, n):
step = pyran.choice(steps)
if step == "EAST":
x[i] = x[i - 1] + 1
y[i] = y[i - 1]
elif step == "WEST":
x[i] = x[i - 1] - 1
y[i] = y[i - 1]
elif step == "NORTH":
x[i] = x[i - 1]
y[i] = y[i - 1] + 1
else:
x[i] = x[i - 1]
y[i] = y[i - 1] - 1
pythonlab.title("Two Dimensional Random Walk")
pythonlab.plot(x, y)
pythonlab.show()
You can execute the above code with the command below:
Execution Command
python3 two_dimension_random_walk.py
The output is the plot which is shown below:

3. Download the Source Code
You can download the full source code of this example here: Random Walk in Python


