Spring MVC Handler Mapping Example
This is an example of how to handle URL requests mapping in Spring MVC. In particular, we shall check on three handler mapping classes that Spring MVC provides for handling URL requests. They are all used to define a mapping between URL requests and handler objects.
We will create a simple project with a Controller, a view (jsp) and we will add the necessary configuration files, and then we will use an application server to run the example, making use of all handler mapping classes.
You may skip project creation and jump directly to the example code section below.
Our preferred development environment is Eclipse. We are using Eclipse Juno (4.2) version, along with Maven Integration plugin version 3.1.0. You can download Eclipse from here and Maven Plugin for Eclipse from here. The installation of Maven plugin for Eclipse is out of the scope of this tutorial and will not be discussed. We are also using JDK 7_u_21. Tomcat 7 is the application server used.
Let’s begin,
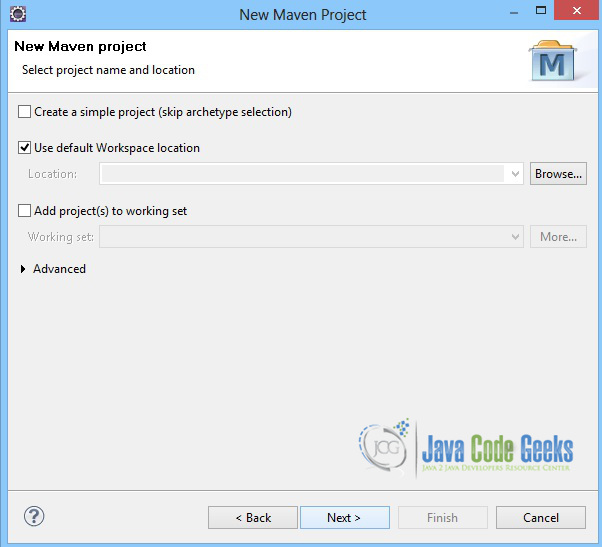
1. Create a new Maven project
Go to File -> Project ->Maven -> Maven Project.
In the “Select project name and location” page of the wizard, make sure that “Create a simple project (skip archetype selection)” option is unchecked, hit “Next” to continue with default values.
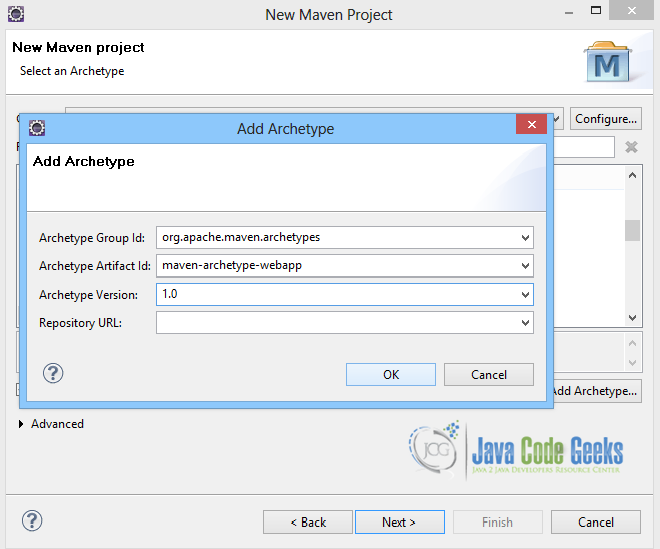
Here the maven archetype for creating a web application must be added. Click on “Add Archetype” and add the archetype. Set the “Archetype Group Id” variable to "org.apache.maven.archetypes", the “Archetype artifact Id” variable to "maven-archetype-webapp" and the “Archetype Version” to "1.0". Click on “OK” to continue.
In the “Enter an artifact id” page of the wizard, you can define the name and main package of your project. Set the “Group Id” variable to "com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise" and the “Artifact Id” variable to "springexample". The aforementioned selections compose the main project package as "com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.springexample" and the project name as "springexample". Set the “Package” variable to "war", so that a war file will be created to be deployed to tomcat server. Hit “Finish” to exit the wizard and to create your project.
The Maven project structure is shown below:
- It consists of the following folders:
- /src/main/java folder, that contains source files for the dynamic content of the application,
- /src/test/java folder contains all source files for unit tests,
- /src/main/resources folder contains configurations files,
- /target folder contains the compiled and packaged deliverables,
- /src/main/resources/webapp/WEB-INF folder contains the deployment descriptors for the Web application ,
- the pom.xml is the project object model (POM) file. The single file that contains all project related configuration.
2. Add Spring-MVC dependencies
Add the dependencies in Maven’s pom.xml file, by editing it at the “Pom.xml” page of the POM editor. The dependency needed for MVC is the spring-webmvc package, and the javax.servlet package as shown below:
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise</groupId>
<artifactId>springexample</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springexample Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>springexample</finalName>
</build>
<properties>
<spring.version>3.2.3.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
</project>
3. Create a Controller – View – Model example
The HelloWorldController extends the AbstractController provided by Spring, and overrides the handleRequestInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) method, where a org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView is created by a handler and returned to be resolved by the DispatcherServlet.
HelloWorldController.java
package com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.AbstractController;
public class HelloWorldController extends AbstractController{
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleRequestInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("helloWorld");
model.addObject("msg", "hello world!");
return model;
}
}
The view is a simple jsp page, that shows the value of the attribute that was set to the HelloWorldController. It must be placed in /WEB-INF/ folder.
helloWorld.jsp
<html>
<body>
<h1>Spring 3.2.3 MVC web service</h1>
<h3>Your message is : ${msg}</h3>
</body>
</html>
The files that we must configure in the application are the web.xml file and the mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml file.
The web.xml file is the file that defines everything about an application that a server needs to know. It is placed in /WEB-INF/ directory of the application. The <servlet> element declares the DispatcherServlet. When the DispatcherServlet is initialized, the framework will try to load the application context from a file named [servlet-name]-servlet.xml located in /WEB-INF/ directory. So, we have created the mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml file, that will be explained below. The <servlet-mapping> element of web.xml file specifies what URLs will be handled by the DispatcherServlet.
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
The mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml is also placed in /WEB-INF directory. The org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver is defined as a bean, and is used as internal resource views resolver, meaning that it will find the jsp and html files in the /WEB-INF/ folder. We can set properties such as prefix or suffix to the view name to generate the final view page URL, as shown below:
mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd">
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
So, after having set a simple MVC application, we can check on the different choices Spring MVC provides to map URL requests to the HelloWorldController.
4. BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
The BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping class maps URL requests to beans names. It is the default handler mapping class, so it is the one created by the DispatcherServlet when Spring cannot find any handler mapping class declared. An example of using the BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping class is shown below. There are two beans declared, the first one’s name is helloWorld.htm and its class is the HelloWorldController. So the BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping will map any helloWorld URL request to this Controller. The second bean’s name is the hello*.htm and its class is also the HelloWorldController. So, in this case, the BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping will map any URL request that starts with hello (such as helloWorld, helloAll) to the HelloWorldController.
mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd">
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"/>
<bean name="/helloWorld.htm"
class="com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.HelloWorldController" />
<bean name="/hello*.htm"
class="com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.HelloWorldController" />
</beans>
So, check what happens when the calling the URL helloWorld.htm:

And here is the case of helloGeeks.htm:

5. ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping
The ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping class uses a convention to determine the mapping between request URLs and the Controller instances that are to handle those requests. In this case, there is no need to declare a bean name for the Controller. In the example below, the ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping will map to the HelloWorldController all URL requests that start with helloWorld, or helloWorld*. In the ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping bean declaration there are two properties to configure, the caseSensitive, which is set to true, and the pathPrefix, which is set to /javacodegeeks/. These properties allow ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping to also map to the HelloWorldController all URL requests with uppercase characters, like helloWorldJavaCodeGeeks, as also URL requests with path prefix like /javacodegeeks/helloWorld.
mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
.... <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping" > <property name="caseSensitive" value="true" /> <property name="pathPrefix" value="/javacodegeeks" /> </bean> <bean class="com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.HelloWorldController" /> ...
The cases described above are shown in the screenshots below.
Here is a case of uppercase characters:
And here is a case with a pathPrefix:
6. SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
The SimpleUrlHandlerMapping provides a property called mappings so as to be configured. This property is set in the bean declaration and consists of key value mapping pairs. It can be set in two ways, as shown below:
mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
.... <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping"> <property name="mappings"> <props> <prop key="/helloWorld.htm">helloWorldController</prop> <prop key="/*/hello.htm">helloWorldController</prop> <prop key="/hello*.htm">helloWorldController</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean id="helloWorldController" class="com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.HelloWorldController" /> ...
mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
.... <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping"> <property name="mappings"> <value> /helloWorld.htm=helloWorldController /*/hello.htm=helloWorldController /hello*.htm=helloWorldController </value> </property> </bean> <bean id="helloWorldController" class="com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.HelloWorldController" /> ....
Note that the Controller bean declaration uses an id property, which is used in the SimpleUrlHandlerMapping bean declaration for the mapping. Each one of the cases configured above, are shown in the screenshots below:
7. Handler mapping priorities
The handler mapping implementations described can be mixed and used together. The only thing that needs to be configured is the priority of each mapping class, so that Spring MVC DispatcherServlet will know which handler mapping implementation to use with what priority. The priority can be set as a property in every mapping bean declaration, as shown below:
mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
... <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping"> <property name="mappings"> <value> /helloWorld.htm=helloWorldController /*/hello.htm=helloWorldController /hello*.htm=helloWorldController </value> </property> <property name="order" value="0" /> </bean> <bean id="helloWorldController" class="com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.HelloWorldController" /> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping" > <property name="caseSensitive" value="true" /> <property name="pathPrefix" value="/javacodegeeks" /> <property name="order" value="1" /> </bean> <bean class="com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.HelloWorldController" /> ...
In this case, both ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping and SimpleUrlHandlerMapping are used, but the first one to handle a URL request will be the SimpleUrlHandlerMapping.
This was an example of how to handle requests mapping in Spring MVC.
Download source code from this tutorial : SpringMVCHandlerMappingExample