Spring MVC Checkbox And Checkboxes Example
This is a simple example of how to create a checkbox and a checkboxes tag in Spring MVC. Among the most famous HTML tags is the checkbox tag, that allows users to check one or more values in a form. Spring MVC checkbox and checkboxes tags are pretty similar to the HTML checkbox tag and they are very easy to use, as will be shown below.
This example contains a simple class, which is the MVC model and has two properties, one boolean property to be used for the checkbox tag and a List of String values to be used for the checkboxes tag. There is also a simple view that contains a form with the checkbox and checkboxes fields.
You may skip project creation and jump directly to the beginning of the example below.
Our preferred development environment is Eclipse. We are using Eclipse Juno (4.2) version, along with Maven Integration plugin version 3.1.0. You can download Eclipse from here and Maven Plugin for Eclipse from here. The installation of Maven plugin for Eclipse is out of the scope of this tutorial and will not be discussed. We are also using JDK 7_u_21. Tomcat 7 is the application server used.
Let’s begin,
1. Create a new Maven project
Go to File -> Project ->Maven -> Maven Project.
In the “Select project name and location” page of the wizard, make sure that “Create a simple project (skip archetype selection)” option is unchecked, hit “Next” to continue with default values.
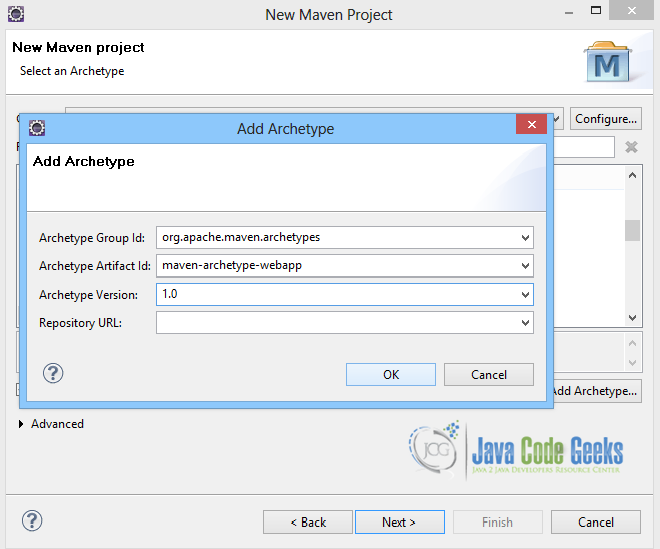
Here the maven archetype for creating a web application must be added. Click on “Add Archetype” and add the archetype. Set the “Archetype Group Id” variable to "org.apache.maven.archetypes", the “Archetype artifact Id” variable to "maven-archetype-webapp" and the “Archetype Version” to "1.0". Click on “OK” to continue.
In the “Enter an artifact id” page of the wizard, you can define the name and main package of your project. Set the “Group Id” variable to "com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise" and the “Artifact Id” variable to "springexample". The aforementioned selections compose the main project package as "com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.springexample" and the project name as "springexample". Set the “Package” variable to "war", so that a war file will be created to be deployed to tomcat server. Hit “Finish” to exit the wizard and to create your project.
The Maven project structure is shown below:
- It consists of the following folders:
- /src/main/java folder, that contains source files for the dynamic content of the application,
- /src/test/java folder contains all source files for unit tests,
- /src/main/resources folder contains configurations files,
- /target folder contains the compiled and packaged deliverables,
- /src/main/resources/webapp/WEB-INF folder contains the deployment descriptors for the Web application ,
- the pom.xml is the project object model (POM) file. The single file that contains all project related configuration.
2. Add Spring-MVC dependencies
Add the dependencies in Maven’s pom.xml file, by editing it at the “Pom.xml” page of the POM editor. The dependency needed for MVC is the spring-webmvc package.
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise</groupId>
<artifactId>springexample</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springexample Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>validation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>5.1.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>springexample</finalName>
</build>
<properties>
<spring.version>3.2.9.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
</project>
3. Create the model
Member.java is a simple Java class, that has two properties, the boolean newMember and a List of Strings, which is the courses. Both fields must have getters and setters, so that they are accessible from the view.
Member.java
package com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.checkbox.model;
import java.util.List;
public class Member {
private boolean newMember;
private List<String> courses;
public boolean isNewMember() {
return newMember;
}
public void setNewMember(boolean newMember) {
this.newMember = newMember;
}
public List<String> getCourses() {
return courses;
}
public void setCourses(List<String> courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
}
4. Create the Controller
The Controller is where the DispatcherServlet will delegate requests. The @Controller annotation indicates that the class serves the role of a Controller. The @RequestMapping annotation is used to map a URL to either an entire class or a particular handler method.
The Controller consists of two basic methods, a GET method, which is String initForm(Model model) and a POST method, which is String submitForm(Model model, Member member, BindingResult result). The first method creates and returns to the "member" view a new instance of the Member.java class. Here, a new List of String values is created to be given as an attribute to the model, so as to be used in the form for the checkboxes items. Note that another list of String values is created that is set to the courses property of the new Member instance. Thus, the model now has pre-checked values.
The second method also gets the Model, and the Member object created, which now consists of the values passed in the form.It returns the String representation of the successMember.jsp page, which also has the values checked on the checkbox.
Member Controller.java
package com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.checkbox;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise.checkbox.model.Member;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/member.htm")
public class MemberController {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String initForm(Model model) {
Member member = new Member();
List<String> preCheckedVals = new ArrayList<String>();
preCheckedVals.add("Yoga");
member.setCourses(preCheckedVals);
model.addAttribute("member", member);
List<String> courses = new ArrayList<String>();
courses.add("Yoga");
courses.add("Stretching");
courses.add("Pilates");
courses.add("Aerobic");
courses.add("Oriental");
model.addAttribute("courses", courses);
return "member";
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String submitForm(Model model, Member member,
BindingResult result) {
model.addAttribute("member", member);
return "successMember";
}
}
5. Create the view with the checkbox and a checkboxes field
The view below is a simple example of how to create a checkbox field and a checkboxes field. It is a simple html view consisting of the head and body html tags. In order to create a form in Spring MVC, we make use of the form:form tag. Its method property is set to POST, and the commandName property is set to the name of the backing bean that is binded to the Model, which is the Member.java class.
The form:checkbox tag is used to create the checkbox field, with its path property set to the field binded to it. The form:checkboxes tag has another property to configure, appart from the path property. It also provides the items property, where the list of the items to be displayed is set. Finally, the input tag, with type property set to submit is used for the submit button.
member.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form"%>
<html>
<title>Spring MVC checkbox</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Subscribe to the gym</h2>
<form:form method="POST" commandName="member">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Are you a new member?</td>
<td><form:checkbox path="newMember" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Choose the courses you like:</td>
<td><form:checkboxes path="courses" items="${courses}" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
</table>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
Below is the page that will be rendered when the Submit button is pressed, It uses the JSP Standard Tag Library to render the items checked in the checkboxes tag.
successMember.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form"%>
<html>
<head>
<title>Spring MVC checkbox</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>The courses you selected are shown below:</h2>
<br>
<c:forEach var="course" items="${member.courses}">
<c:out value="${course}"/><br>
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>
6. Configure the application
The files that we must configure in the application are the web.xml file and the mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml file.
The web.xml file is the file that defines everything about the application that a server needs to know. It is placed in the /WEB-INF/ directory of the application. The <servlet> element declares the DispatcherServlet. When the DispatcherServlet is initialized, the framework will try to load the application context from a file named [servlet-name]-servlet.xml located in /WEB-INF/ directory. So, we have created the mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml file, that will be explained below. The <servlet-mapping> element of web.xml file specifies what URLs will be handled by the DispatcherServlet.
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
The mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml file is also placed in WebContent/WEB-INF directory. The org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver bean is used as internal resource views resolver, meaning that it will find the jsp and html files in the WebContent/WEB-INF/ folder. We can also set properties such as prefix or suffix to the view name to generate the final view page URL. This is the file where all beans created, such as Controllers are placed and defined.
The <context:component-scan> tag is used, so that the Spring container will search for all annotated classes under the com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise package. The <mvc:annotation-driven> tag is used, so that the container searches for annotated classes, to resolve MVC.
mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.javacodegeeks.snippets.enterprise" /> <mvc:annotation-driven /> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix"> <value>/WEB-INF/</value> </property> <property name="suffix"> <value>.jsp</value> </property> </bean> </beans>
7. Run the application
Now, let’s run the application. We first build the project with Maven. All we have to do is right click on the project and select -> Run As: Maven build. The goal must be set to package. The .war file produced must be placed in webapps folder of tomcat. Then, we can start the server.
Hit on:
http://localhost:8080/springexample/member.htm
As you may see, the “Yoga” box is pre-checked. You can choose one or more boxes and click on Submit:
Here, you can take a look at the courses you chose.
This was an example of how to use checkbox and checkboxes tags in Spring MVC.
Download the eclipse project of this tutorial: SpringMVCCheckbox